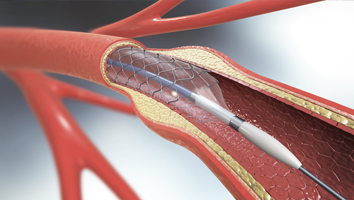
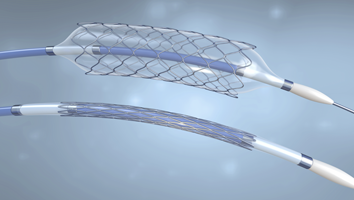
Cardiac Care
Your heart is the relentless engine driving your life's journey, fueling every moment with vitality. If you're facing cardiac challenges, know that there's a path to a healthier, more vibrant future. Welcome to our patient education resource on cardiac care and interventions. Here, we'll empower you with essential knowledge and inspire you to embrace the possibilities of a heart-healthy, fulfilling life.
Cardiac Care Information