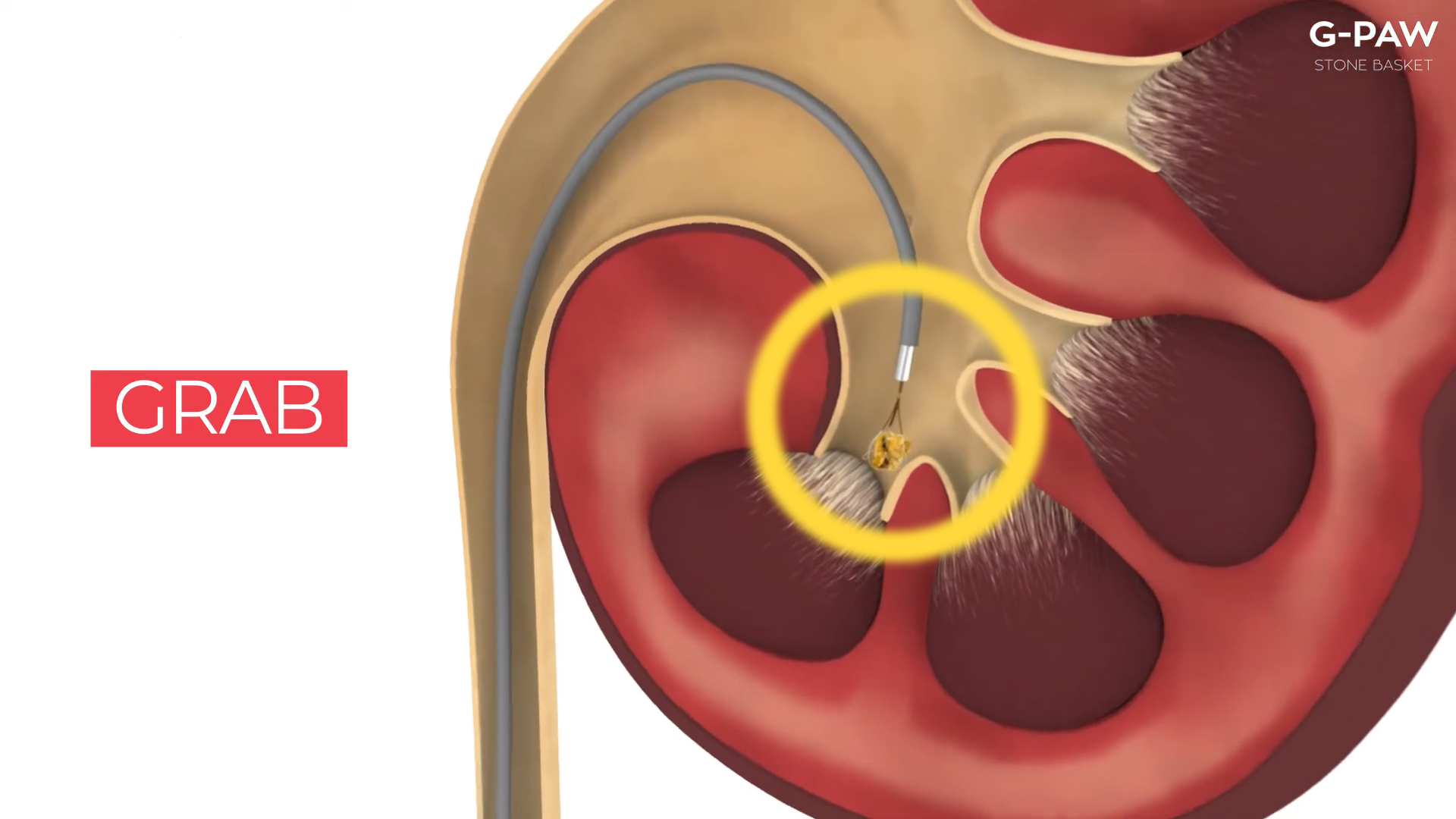
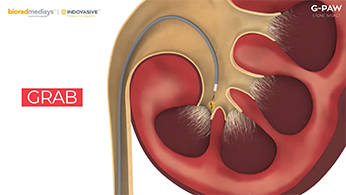
Retrograde intrarenal surgical operation (RIRS) is a process undertaken as a surgical treatment within the kidney with the usage of a viewing tube called a fibrotic endoscope.
In the RIRS surgery, the scope is inserted in the body through the urethra (the urinary establishing) into the urinary bladder and then it passes through the ureter into the urine-amassing part of the kidney. The scope in this process is moved retrograde (up the urinary tract device) to inside the kidney (intrarenal).
RIRS is executed to cast off a kidney stone. The stone is seen through the scope and might then be manipulated or crushed by using an ultrasound probe or evaporated by a laser probe or grabbed through small forceps, and so on.
RIRS is executed with the aid of a consultant, urologist (endourologist) with significant experience in performing RIRS surgeries. The process is generally carried out underneath general or spinal anesthesia.
There are several benefits of the RIRS surgery with the major ones stated as follows:
- RIRS is considered to be the SAFEST surgery for kidney stones as it is a no-cut procedure.
- Recovery time after RIRS is considered to the FASTEST compared to other alternatives.
- It is a minimally invasive surgery.
- All types of kidney stones can be treated through RIRS, unlike lithotripsy where certain compositions are resistant.
- RIRS is considered to be a straightforward and faster method of surgery for kidney stones.
- There is no danger to the renal tissue throughout and post-surgery RIRS eliminates prolonged pain after surgery.
- The surgery is considered to be less painful and involves minimal or no blood loss.
- Lesser chances of morbidities post-surgery.











Leave a comment