Knee pain, a pervasive issue affecting millions worldwide, can significantly impede daily life. When conservative treatments fall short, knee replacement surgery emerges as a transformative solution, offering relief from persistent pain and a chance to regain lost mobility. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes of knee pain that often lead to knee replacement surgery, the precautions necessary for a successful recovery post-surgery, and conclude with reflections on the life-changing impact of this medical intervention.
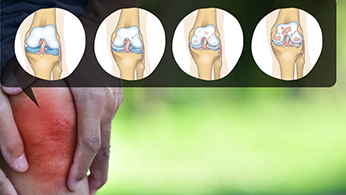
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis stands out as the leading cause of knee pain that frequently leads to knee replacement surgery. Wearing down of the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones causes this degenerative joint disease. As the cartilage diminishes, bones rub against each other, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. Osteoarthritis is often associated with aging, but it can also be accelerated by genetic factors, joint injuries, and obesity.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder, is another contributor to knee pain necessitating surgical intervention. In this condition, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium—a membrane lining the joint. As a result of the persistent inflammation, joints are damaged, painful, and swollen. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is primarily age-related, rheumatoid arthritis can affect individuals of any age, making it a significant factor in the decision to undergo knee replacement surgery.
- Traumatic Injuries: Traumatic injuries, such as fractures or ligament tears, can hasten the degeneration of the knee joint. Athletes, in particular, are susceptible to such injuries due to the repetitive stress placed on their knee joints during physical activities. If these injuries are not adequately addressed, they can set the stage for arthritis, prompting the need for knee replacement surgery.
- Other Conditions: Various medical conditions, including avascular necrosis, gout, and certain infections, can contribute to the breakdown of the knee joint, leading to chronic pain and diminished functionality. While these conditions may not be as common as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, they underscore the diverse range of factors that can necessitate knee replacement surgery.
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: Post-surgery, rehabilitation and physical therapy play pivotal roles in the recovery process. A tailored rehabilitation program is designed to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the knee. Patients are encouraged to actively participate in exercises and stretches that are gradually intensified as the healing progresses. The guidance of skilled physical therapists is invaluable in ensuring a smooth recovery trajectory.
- Medication Management: Pain management is a critical component of the post-surgery phase. Patients are typically prescribed pain medications to alleviate discomfort and facilitate engagement in rehabilitation exercises. It is imperative to strictly adhere to the prescribed dosage and consult with healthcare providers before making any adjustments to the medication regimen. Balancing pain relief with mindful medication use is key to a successful recovery.
- Activity Modification: During the initial stages of recovery, patients are advised to modify their activities to avoid high-impact exercises and excessive stress on the replaced knee. A gradual reintroduction of activities is typically guided by the healthcare team based on individual progress. This cautious approach minimizes the risk of complications, ensures a smoother recovery, and promotes the longevity of the knee replacement.
- Follow-up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with the orthopedic surgeon are essential for monitoring the healing process and addressing any emerging concerns. X-rays and imaging tests may be conducted to assess the implant’s position and overall joint health. Any signs of infection, swelling, or unusual discomfort should be promptly reported to the healthcare provider, emphasizing the importance of vigilant follow-up care.
- Lifestyle Modifications: A holistic approach to recovery involves adopting a healthy lifestyle. Maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and managing weight are crucial factors that positively impact joint health. Smoking cessation is also strongly recommended, as smoking can impair the body’s ability to heal and increase the risk of complications. These lifestyle modifications contribute significantly to the overall success and longevity of the knee replacement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knee replacement surgery stands as a beacon of hope for individuals grappling with chronic knee pain and compromised mobility. Whether stemming from osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic injuries, or other conditions, the decision to undergo knee replacement surgery is often a transformative one. The road to recovery requires dedication to rehabilitation, prudent medication management, thoughtful activity modification, regular follow-up care, and sustained lifestyle modifications.
As patients navigate this multifaceted journey, they discover the potential for renewed vitality and the joy of pain-free movement. Knee replacement surgery not only addresses the physical aspects of joint deterioration but also opens doors to a more active, fulfilling life. By understanding the causes of knee pain leading to surgery and embracing the precautions necessary for a successful recovery, individuals embark on a path toward reclaiming their mobility and rediscovering the pleasures of unrestricted movement.











Leave a comment